SEMANTIC SEGMENTATION WITH PIXELLIB¶
PixelLib is implemented with Deeplabv3+ framework to perform semantic segmentation. Xception model trained on pascalvoc dataset is used for semantic segmentation.
Download the xception model from here.
Code to implement semantic segmentation:
import pixellib
from pixellib.semantic import semantic_segmentation
segment_image = semantic_segmentation()
segment_image.load_pascalvoc_model("deeplabv3_xception_tf_dim_ordering_tf_kernels.h5")
segment_image.segmentAsPascalvoc("path_to_image", output_image_name = "path_to_output_image")
We shall take a look into each line of code.
import pixellib
from pixellib.semantic import semantic_segmentation
#created an instance of semantic segmentation class
segment_image = semantic_segmentation()
The class for performing semantic segmentation is imported from pixellib and we created an instance of the class.
segment_image.load_pascalvoc_model("deeplabv3_xception_tf_dim_ordering_tf_kernels.h5")
We called the function to load the xception model trained on pascal voc.
segment_image.segmentAsPascalvoc("path_to_image", output_image_name = "path_to_output_image")
This is the line of code that performs segmentation on an image and the segmentation is done in the pascalvoc’s color format. This function takes in two parameters:
path_to_image: the path to the image to be segemented.
path_to_output_image: the path to save the output image. The image will be saved in your current working directory.
Sample1.jpg
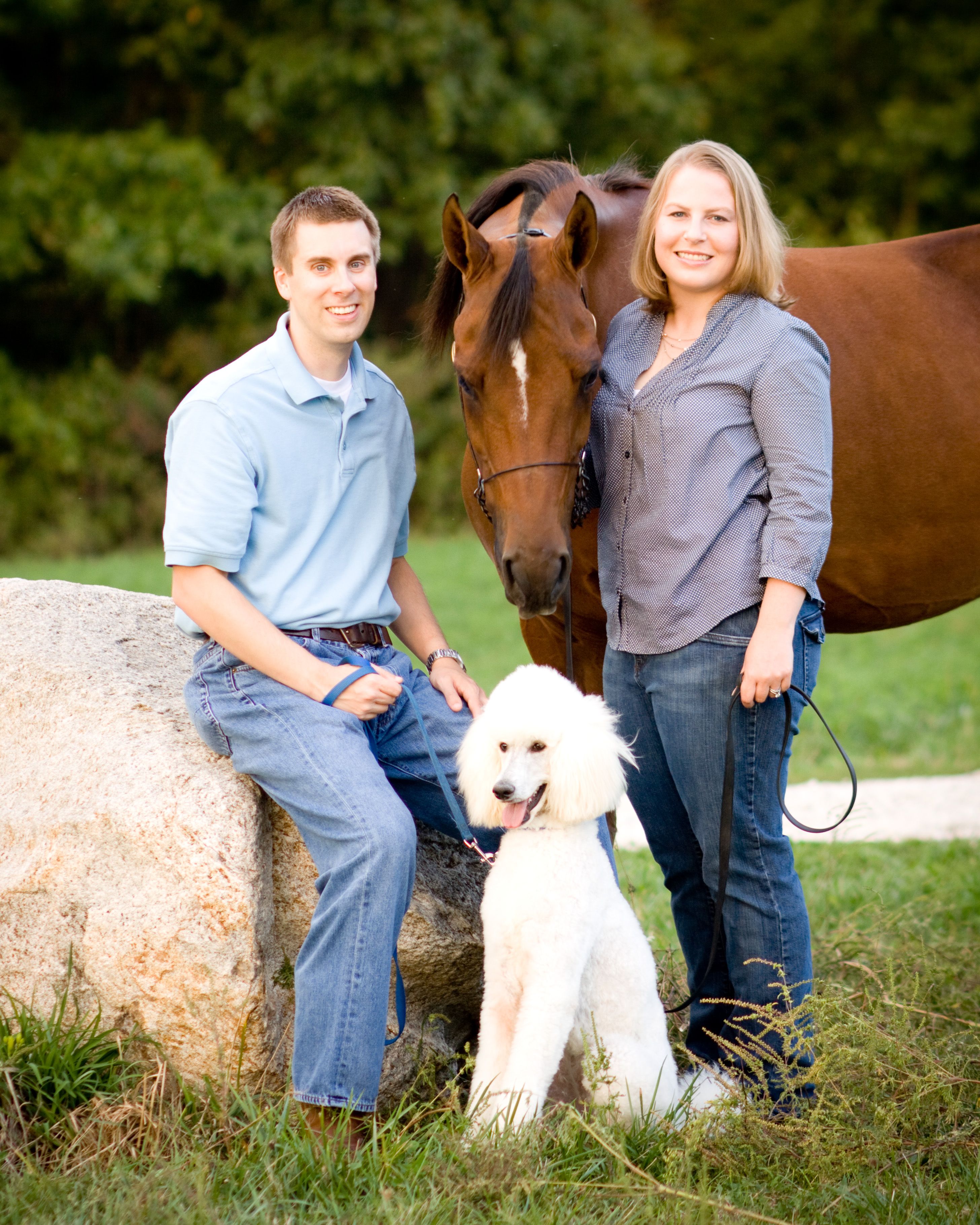

Image’s source: Pinterest
import pixellib
from pixellib.semantic import semantic_segmentation
segment_image = semantic_segmentation()
segment_image.load_pascalvoc_model("deeplabv3_xception_tf_dim_ordering_tf_kernels.h5")
segment_image.segmentAsPascalvoc("sample1.jpg", output_image_name = "image_new.jpg")
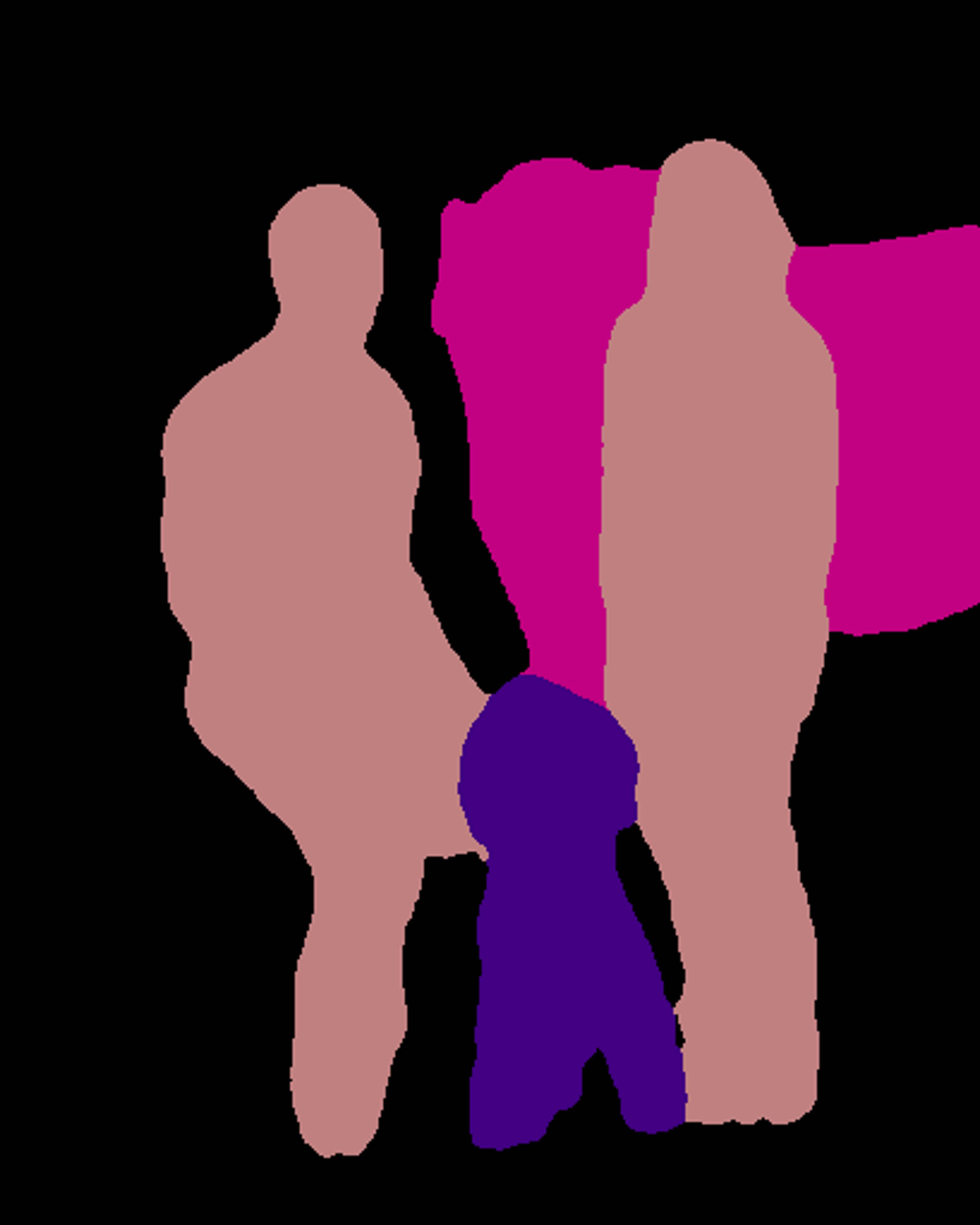
Your saved image with all the objects present segmented.
You can obtain an image with segmentation overlay on the objects with a modified code below.
segment_image.segmentAsPascalvoc("sample1.jpg", output_image_name = "image_new.jpg", overlay = True)
We added an extra parameter overlay and set it to true, we produced an image with segmentation overlay.
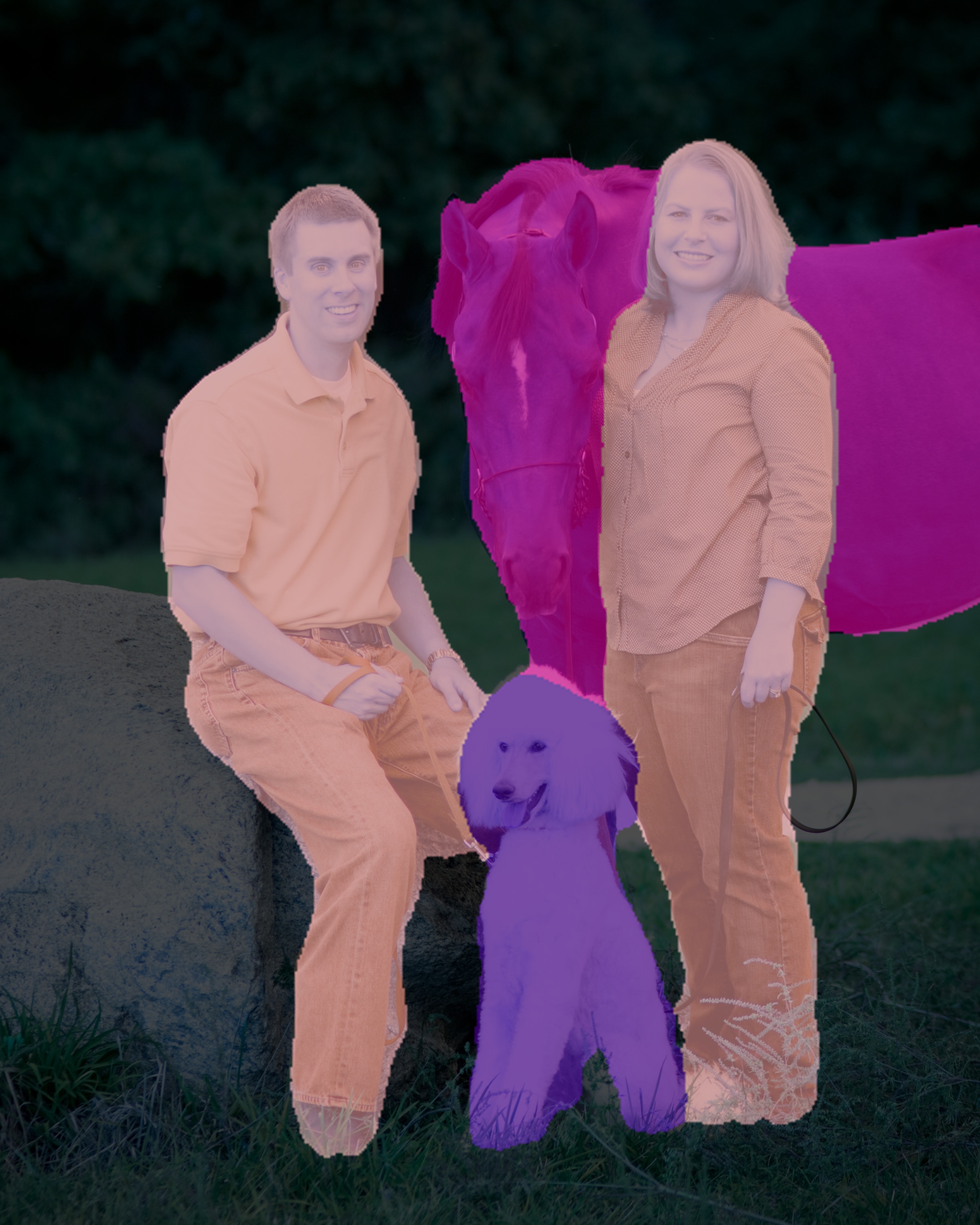

- You can check the inference time required for performing segmentation by modifying the code below..
import pixellib
from pixellib.semantic import semantic_segmentation
import time
segment_image = semantic_segmentation()
segment_image.load_pascalvoc_model("pascal.h5")
start = time.time()
segment_image.segmentAsPascalvoc("sample1.jpg", output_image_name= "image_new.jpg")
end = time.time()
print(f"Inference Time: {end-start:.2f}seconds")
Inference Time: 8.19seconds
It took 8.19 seconds to run semantic segmentation on the image.
Specialised uses of PixelLib may require you to return the array of the segmentation’s output.
- Obtain the array of the segmentation’s output by using this code,
output, segmap = segment_image.segmentAsPascalvoc()
- You can test the code for obtaining arrays and print out the shape of the output by modifying the semantic segmentation code below.
import pixellib
from pixellib.semantic import semantic_segmentation
import cv2
segment_image = semantic_segmentation()
segment_image.load_pascalvoc_model("pascal.h5")
output, segmap = segment_image.segmentAsPascalvoc("sample1.jpg")
cv2.imwrite("img.jpg", output)
print(output.shape)
- Obtain both the output and the segmentation overlay’s arrays by using this code,
output, segoverlay = segment_image.segmentAsPascalvoc(overlay = True)
import pixellib
from pixellib.semantic import semantic_segmentation
import cv2
segment_image = semantic_segmentation()
segment_image.load_pascalvoc_model("pascal.h5")
segmap, segoverlay = segment_image.segmentAsPascalvoc("sample1.jpg", overlay= True)
cv2.imwrite("img.jpg", segoverlay)
print(segoverlay.shape)
This xception model is trained on pascal voc dataset, a dataset with 20 object categories.
Objects and their corresponding colormaps.
